Intelligent anti-microbial system (i.A.M.S)
Research & Innovation
Intelligent anti-microbial system (i.A.M.S)
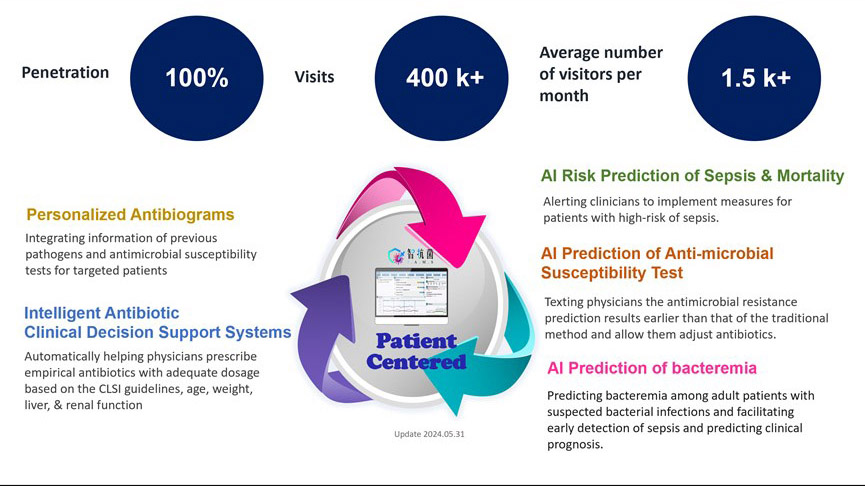
AI prediction of microbial resistance, personalized antibiogram, antibiotics decision support system, risk of sepsis and mortality AI prediction
Sepsis impacts millions of people and causes millions of countless deaths annually worldwide, including Taiwan. The mortality could can be up toas high as 29.2%. Failure to detect and diagnose sepsis early is an important significant factor for to the high mortality rate. Per For each hour of delay in appropriate antibiotic administration, the mortality rate increases by 7.6%. Additionally, the extended- and pan-drug resistant bacteria, known as “superbugs,” spread rapidly globally. The World Health Organization (WHO) reported that approximately 700 000 individuals died from infectious disease caused by resistant bacteria, and approximately 10,000,000 individuals would are projected to die due to “superbug” infections byin 2050, which would have a greater impacts more than that of COVID-19. “Optimizing antibiotics usage and developing rapid tests” are important issue in antimicrobial stewardship. However, the critical conditions changed more rapidly than that of the traditional methods canto identify pathogens and antimicrobial susceptibilities.
In order to resolveTo address these problems, our team produced developed the first and most complete “comprehensive antimicrobial system” that focusinges on patients with infections and sepsis. The team is composed of specialists inthe infectious disease and critical care medicine-specialized physicians, the Laboratory Medicine Department, the Pharmacy Department, the Information Technology Department, the Big Data Center, and the Artificial Intelligence Center. We organize the big data and information and use the AI prediction to help clinicians diagnose more rapidly and perform precise therapy.
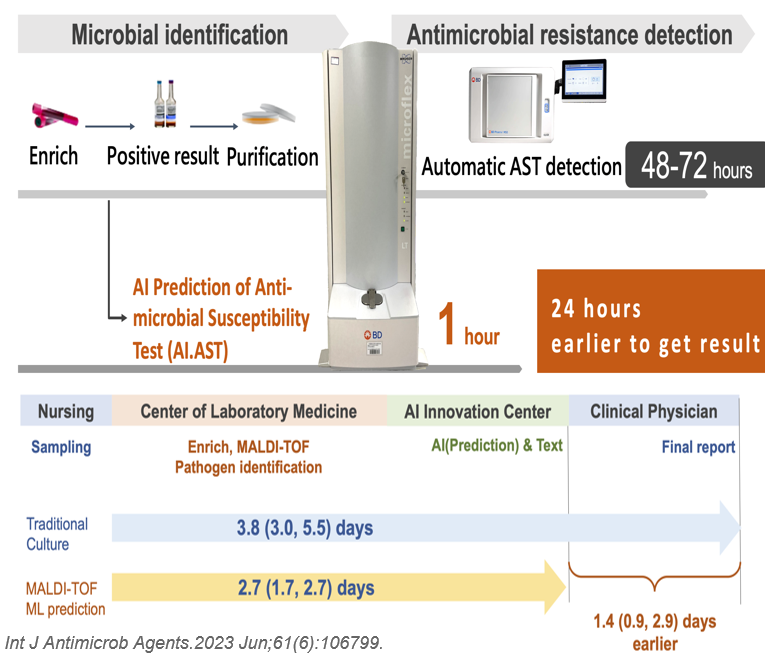
The “prediction of sepsis risks and mortality” alerts clinicians to implement measures for high-risk patients with high risk. Clinicians canould obtain information from previous pathogens and antimicrobial susceptibility tests for targeted patients throughby “personized antibiograms,” and fromthe locally common pathogens with antimicrobial susceptibility through theby “intelligent antibiotic clinical decision support systems.” Furthermore, the systems also help physicians prescribe empirical antibiotics with adequate dosage based on the patient’sthe weight, liver, and renal function. “AI prediction of antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST)” could informtext physicians ofthe antimicrobial resistance prediction results earlier than that of the traditional methods, and allowing them to adjust antibiotics promptly.
We integrated the scattered data over time, AI prediction of sepsis, and AST in a user-friendly platform to achieve early sepsis detection, more rapid pathogen and antimicrobial susceptibility identification, and appropriate antibiotics use. Based on the “comprehensive antimicrobial system,” our team aims to would offer more personalized, precision medicine in a timely manner, with higher quality combined with gene information.
The i.A.M.S platform comprisesis composed of 5 critical major functions: an AI sepsis prediction system, a rapid antibiotic resistance prediction system, a personalized antibiograms, AI predication of bacteremia, and an antibiotic clinical decision support system (CDSS). The CDSS includes automated dosage calculations, intravenous flow rate calculations, the volume of diluted liquid, antibiotic recommendations, and drug allergy notes . The systems can be integrated into electronic medical records (EMRs) and provide alerts through event-driven design, allowing health care information systems (HISs) and AI to communicate in real time.