Minimally Invasive Surgery Center
Research & Innovation
Minimally Invasive Surgery Center
The robot arm surgery system combines computer and robot technology to create a new surgical method. Robot-arm-assisted laparoscopic and thoracoscopic surgery provide surgeons more choices and expand the scope of minimally invasive surgery. The Da Vinci robotic surgery system has been used in many different surgical fields, including various types of minimally invasive tumor resection and reconstructive repair surgery. The system can perform major surgery in the abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity or chest cavity through several small incisions. In addition, surgeons can perform surgery more precisely and dexterously through better 3D stereo images than traditional laparoscopic surgery and surgical instruments that rotate as flexibly as wrist joints. Besides, the MAKOplasty artificial joint replacement and Robotic stereotactic assistance system (ROSA) are also helpful in the orthopedic surgery and neurosurgery in CMUH.
Directors Huang and Lin get the certification as observation center from the original manufactory of Da Vinci Surgical system.
|
Category
|
Department
|
As off 2024.01
|
Sum
|
|
|
Da Vinci surgical system
(Since 2012.02) |
Urology
|
2,320
|
3,895
|
|
|
Obstetrics & Gynecology
|
630
|
|||
|
ENT, head & neck surgery
|
414
|
|||
|
Department of surgery
(255) |
General surgery
|
67
|
||
|
Colorectal surgery
|
343
|
|||
|
Thoracic surgery
|
70
|
|||
|
Cardiovascular surgery
|
48
|
|||
|
Breast surgical oncology
|
3
|
|||
|
MAKOplasty artificial joint replacement (Since 2015.01)
|
Orthopedics
|
434
|
434
|
|
|
Robotic stereotactic assistance system (ROSA) ( Since 2022.03)
|
Neurosurgery
|
47
|
174
|
|
|
Orthopedics
|
127
|
|||
Da Vinci surgical system
Product Intro
China Medical University Hospital introduced the third generation da Vinci Surgical System in early 2012, marking a new era in minimally invasive surgery at our institution. The da Vinci robotic arm system offers surgeons an intuitive 3D stereoscopic view, with a tenfold magnification combined with high-resolution imaging. Paired with instruments that mimic the flexibility of the human wrist, this system enables surgeons to perform a variety of operations such as resection, or reconstruction through a few small incisions on the skin, accessing the narrow and complex spaces within the thoracic/abdominal or oral cavity.
In recent years, the da Vinci robotic arm system has become increasingly common in various surgical specialties including gynecology, urology, general surgery, otolaryngology, colorectal surgery, thoracic surgery, and cardiovascular surgery. These procedures are characterized by minimal bleeding, rapid recovery, and precise removal and reconstruction. Our da Vinci Center performs over 350 da Vinci surgeries annually, with a growing number each year, including international patients from the United States, Canada, Europe, Australia, Japan, Singapore, and China. Currently, the Ministry of Health and Welfare has approved National Health Insurance payments for da Vinci surgical procedures for prostate cancer radical removal and partial nephrectomy; our urology and gynecology medical teams have passed the da Vinci surgery international manufacturer certification, becoming a da Vinci surgery observation center for urologic tumors (kidney/bladder/prostate cancer) and gynecologic cancer surgeries.
In 2021, our hospital introduced the latest fourth generation da Vinci Surgical System (Da Vinci Xi), featuring laser and voice-guided precision positioning, along with a fluorescent imaging system for real-time identification. This allows surgeons to operate more flexibly and achieve comprehensive removal of tumors and malignant tissues. Additionally, it is equipped with the world's first computer-assisted automatic surgical suturing feature, significantly reducing surgical complications and offering patients advanced minimally invasive surgical options with smaller incisions, less pain, less blood loss, and faster recovery.
Achievement


MAKO plasty
Product Intro
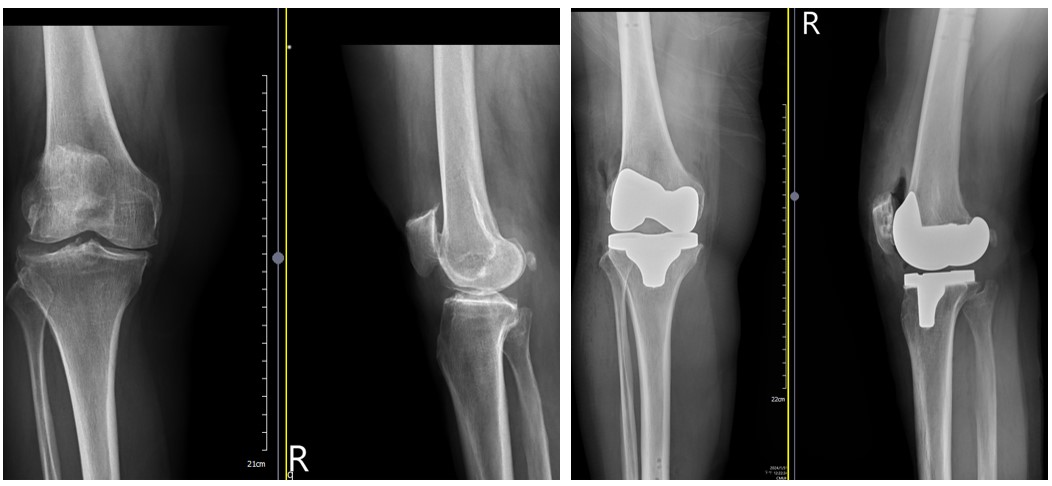
Traditional joint replacement surgery relies mostly on the experience of the surgeon to determine the position and length of the joint replacement. Due to variations in patient characteristics and surgeon experience, there may be a certain degree of error. In contrast, with the assistance of a robotic arm during joint replacement surgery, a preoperative planning is conducted based on computed tomography (CT) scans to create a 3D joint model. This allows for precise and comprehensive preoperative planning. During the surgery, the surgeon operates the robotic arm to perform precise bone cuts and accurately place the artificial joint, thereby reducing the probability of subjective judgment errors and minimizing the occurrence of leg length discrepancy.
Our hospital utilizes the anterior approach joint surgery and the Makoplasty robotic arm, which minimizes damage to muscles, allowing most patients to walk on the day of surgery. Precise preoperative planning and execution during surgery are the cornerstones to ensure successful hip joint replacement. Currently, our hospital has performed over 400 cases of robotic arm joint replacement surgeries, making us the hospital with the highest number of such surgeries in the central region, and we have achieved good and stable outcomes.
Achievement
Contact Information
Orthopedic department/1502/032303@tool.caaumed.org.tw
Robotic stereotactic assistance system (ROSA) Spine
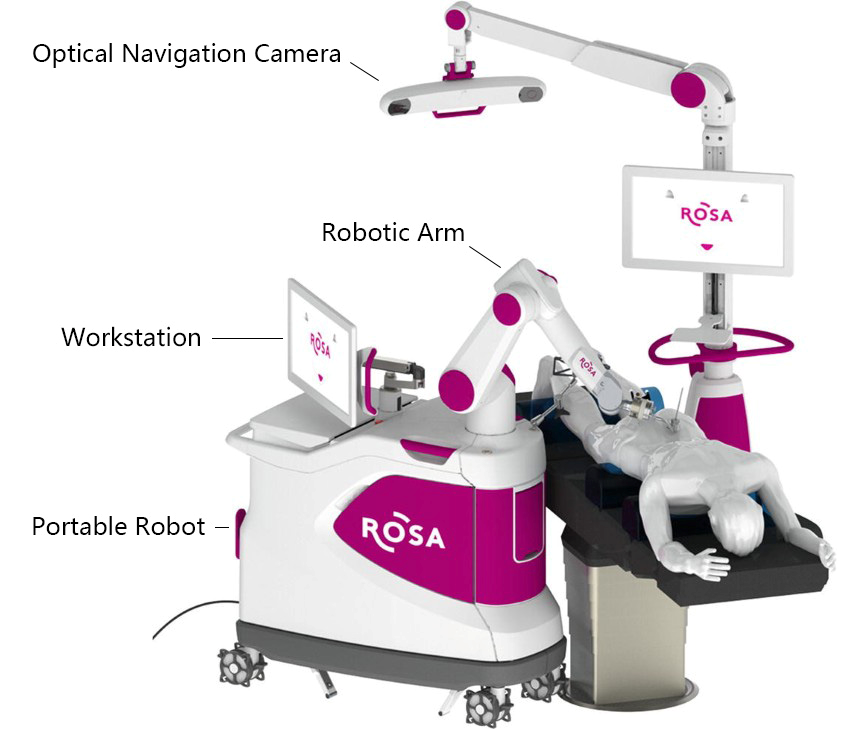
With the development and maturity of stereotactic technology, image fusion, and navigation techniques, neurosurgical spinal surgery robotic systems have emerged, accelerating the promotion and application of precise spinal surgery. In 2021, our neurosurgery department introduced the ROSA® Spine (Medtech) spinal surgery robot, which assists surgeons in minimally invasive spine surgery. The device consists of a protal robot (with a robotic arm and workstation) and an optical navigation camera, allowing ROSA® Spine to accurately place vertebral screws. Robot-assisted screw insertion significantly increases accuracy compared to manual insertion methods, reducing the risk of resivional surgeries, bleeding, and neural damage.
Utilizing its robotic arm and navigation capabilities, the robot monitors spinal movements throughout the procedure, enabling precise and safe operation under the surgeon's instructions. It can also be applied in the treatment of degenerative lumbar disc diseases.
The applications of ROSA® Spine include:
- Assistance in various aspects of the spine surgeries.
- Enhancement of planning capabilities, virtualizing the entire spinal surgery procedure.
- Applicability to almost any percutaneous spine surgery, such as percutaneous screw placments, percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy, intervertebral implant positioning, laminectomy, or radiofrequency ablation surgery.
Spinal surgery robots effectively address issues such as lengthy surgery durations and high experience requirements, reducing surgical trauma, improving surgical precision, and providing patients with safer and more effective surgical options. Our neurosurgery department is the first in Taiwan to obtain the Special Regulation for Cell Therapy and has conducted spinal cord injury stem cell therapy (approved on May 5, 2021). In the future, the robotic arm will be utilized to precisely implant stem cells in patients with spinal cord injuries.